Table of Contents:
- A Simple Guide To Image Formats On The Web
- Modern Image Formats – WebP
- Some of the advantages of this format include:
- Images in the PNG (Portable Network Graphics) format:
- The most common and widely used format, JPG:
- Some advantages of this format include:
- A Simple Guide To Image Formats On The Web
- Conclusion
Last updated December 5th, 2023 23:15
The graphics on a website are a crucial element that often determines the overall user experience of people visiting your website. It is, therefore, very important to use the right types of images based on the purpose they will serve on the web. Nowadays, there are many formats to choose from, but the key ones (aside from SVG for vector graphics) are still JPG, PNG, and WebP formats. So, what are the differences in image formats for the web? A This simple guide to image formats on the web take a closer look at these three formats.
A Simple Guide To Image Formats On The Web
We’ll start gradually from the newest format and work our way to the oldest. The most recent and, so far, the “most modern” format is WebP. It offers many advantages and few disadvantages. Developers particularly appreciate it for websites where speed and reduced data usage are essential. Let’s take a closer look at the mentioned formats one by one.
Modern Image Formats – WebP
This image format was developed by Google in 2010. It offers many advantages, with size being the key benefit for web designers. Compressing images into the WebP format allows you to save a significant amount of space while maintaining relatively similar or comparable image quality. It often happens that an image in WebP format is around 90% smaller than its equivalent in PNG format.
WebP was designed to provide high-quality image compression with minimal loss. As a result, images in this format load much faster. Users can access the desired content in a shorter time frame, and, for instance, save a significant amount of data on their data plan. Faster data loading can also lead to a better website ranking, for example, in search engines like Google.
Another crucial factor is the support for the WebP format in modern browsers. Most major browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Opera, fully support this format. The only issue you might encounter is with older browsers like Internet Explorer.
Some of the advantages of this format include:
- Significantly smaller image sizes compared to older PNG and JPG formats.
- Support in all modern web browsers.
- Support for both lossy and lossless compression.
- The ability to set transparency, similar to the PNG format.
- WebP supports an alpha channel, allowing the use of WebP images for animations and compositions.
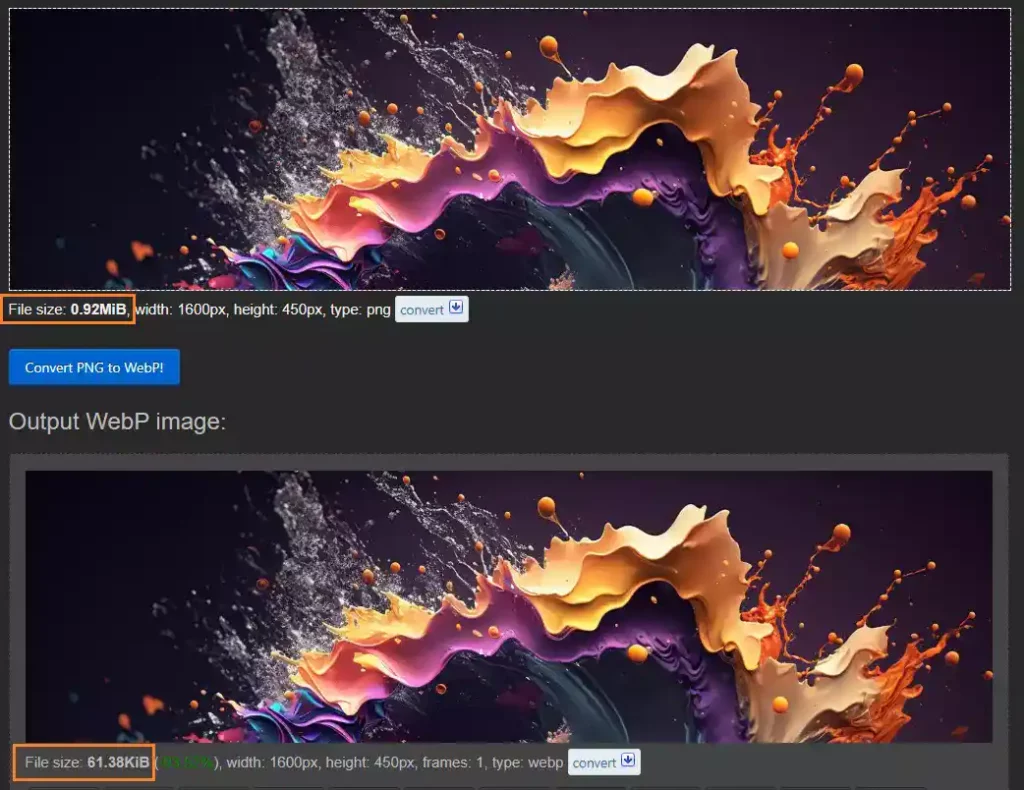
Images in the PNG (Portable Network Graphics) format:
PNG images are a format developed in 1995. They are a lossless format, which means that in this case, image compression doesn’t result in a loss of quality. PNG images are commonly used for icons, logos, and other graphic elements that require transparency. Transparency in PNG images is achieved through an alpha channel, which determines the transparency of individual pixels in the image.
Compared to the newer WebP format mentioned above, PNG images are significantly larger, often by more than 90% for the same image. Web developers and designers often choose the PNG format for graphics that require preserving quality and transparency. In terms of support, nearly all modern browsers can display PNG images without any issues, making it a universal choice for high-quality graphics on the web.
Some advantages of this format include:
- No loss of image quality during compression.
- Support from the vast majority of web browsers.
- Smaller file sizes for images compared to the JPEG format.
- Support for lossless compression.
The most common and widely used format, JPG:
The JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) format, often abbreviated as JPG, is one of the most common and widespread image formats in the world. Its popularity stems from several significant features that make it suitable for a wide range of applications.
One of the key features of the JPG format is its image compression capability. JPEG uses lossy compression, which means it allows for file size reduction by removing some details that the human eye may not perceive. This is particularly useful for photographs, where you can significantly reduce file sizes while maintaining acceptable image quality.
Another advantage of the JPG format is its compatibility and support. Almost all web browsers and graphic programs on the market allow you to open and edit JPG files. This makes it a universal choice for sharing and publishing images on the internet.
The JPG (JPEG) format does not support transparency. It has a solid background and cannot contain transparent areas. For images with transparency, the PNG format is more suitable, as it allows you to save images with an alpha channel responsible for transparency.
Some advantages of this format include:
- Supports a wide spectrum of colors.
- Easily convertible to other formats.
- Has a broad base of supported browsers.
- Suitable for color-rich images.
A Simple Guide To Image Formats On The Web
Conclusion
As you can see, each image format has its positives, and it’s always up to the web developer’s decision regarding which image format to use on the web. For fast-loading websites, the WebP format is suitable, while for higher quality, you might opt for PNG or JPG. However, this higher quality comes at the cost of larger image sizes, which can be up to 9 times larger than the newer WebP format.
So, if you aim for the best scores in tools like PageSpeed Insights and minimal data usage, you can go with the WebP format. If image quality is your primary concern, you can use the other two formats. However, keep in mind that a website, and consequently, the user, may have to load data of many megabytes. This affects website speed, especially on lower-quality mobile connections.
With the WebP format, you should also consider that if a user visits your website with a very old browser, the images may not display at all. It’s a good practice to combine formats so that modern browsers work with the new-generation format, while older browsers still have access to older image formats.
The website is created with care for the included information. I strive to provide high-quality and useful content that helps or inspires others. If you are satisfied with my work and would like to support me, you can do so through simple options.
Byl pro Vás tento článek užitečný?
Klikni na počet hvězd pro hlasování.
Průměrné hodnocení. 0 / 5. Počet hlasování: 0
Zatím nehodnoceno! Buďte první
Je mi líto, že pro Vás nebyl článek užitečný.
Jak mohu vylepšit článek?
Řekněte mi, jak jej mohu zlepšit.

Subscribe to the Newsletter
Stay informed! Join our newsletter subscription and be the first to receive the latest information directly to your email inbox. Follow updates, exclusive events, and inspiring content, all delivered straight to your email.
Are you interested in the WordPress content management system? Then you’ll definitely be interested in its security as well. Below, you’ll find a complete WordPress security guide available for free.

