Table of Contents:
- Installation and Configuration of Netdata on Ubuntu Server
- Installation
- Configuration
- Firewall Configuration
- Installation and configuration of Netdata on Ubuntu server – Conclusion
Last updated December 6th, 2023 00:25
Netdata is an open-source software designed for real-time monitoring of your server. With this software, you can view and collect data about the performance of your server and its various components in real-time. You can monitor CPU load, memory, disks, network traffic, and much more. The installation and configuration of Netdata on Ubuntu server are straightforward and take only a few minutes. The monitoring is accessible through a web browser by entering the server’s IP address and port 19999.
Installation and Configuration of Netdata on Ubuntu Server
Installation
To set up monitoring on your server, first log in via SSH and enter the following two commands.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install netdata
The command ‘sudo apt update’ is used to update the list of available packages in your system from APT (Advanced Package Tool) repositories. The second command will perform the actual installation of the tool. During the installation, you will need to confirm it (by pressing the letter ‘y’ for yes and then pressing Enter to confirm the choice).
Configuration
Now, choose your favorite text editor to modify the Netdata configuration file. This file is located at /etc/netdata/netdata.conf. In the example, we will use the nano editor. You can use your preferred editor, such as vim.
sudo nano /etc/netdata/netdata.conf
Once the editor starts, you will be interested in this section of the configuration file:
run as user = netdata
web files owner = root
web files group = root
bind socket to IP = 127.O.O.O
In this section, modify the ‘bind socket’ line and replace the localhost address with the IP address of your server. Save the edited configuration file. In the nano editor, you can save the file by pressing the CTRL+X key combination. Then confirm the file modification by pressing ‘y’ and pressing the Enter key.
Firewall Configuration
If you have the UFW firewall enabled on your server, you will also need to add a rule to allow access to port 19999. You can set up two types of rules in the firewall. The first rule allows access to the monitoring from anywhere, while the second rule allows monitoring only from a specific IP address. I highly recommend using the second rule, keeping the monitoring hidden behind the firewall and accessible only from your defined IP address (e.g., home or work). You can find your current IP address on the website myip.com.
Rule to allow monitoring from anywhere.
sudo ufw allow 19999
Rule to keep monitoring hidden behind the firewall and accessible only from a pre-defined IP address. Change the IP address 123.123.123.123 to your own.
sudo ufw allow from 123.123.123.123 to any port 19999
Installation and configuration of Netdata on Ubuntu server – Conclusion
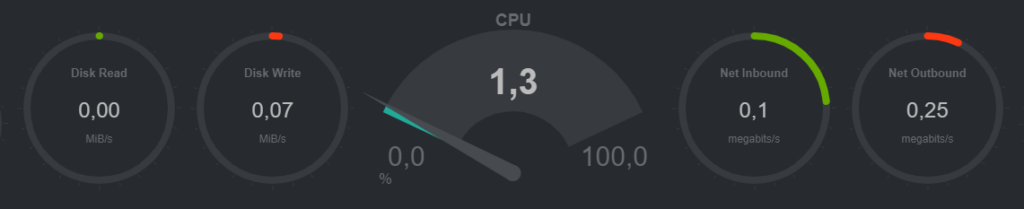
And that’s it. Now your monitoring is accessible at http://123.123.123.123:19999. Of course, you should modify the IP address in the URL to match your server’s IP address. Finally, I’m attaching a few screenshots from the interface so you can get an idea of what the monitoring looks like.
The website is created with care for the included information. I strive to provide high-quality and useful content that helps or inspires others. If you are satisfied with my work and would like to support me, you can do so through simple options.
Byl pro Vás tento článek užitečný?
Klikni na počet hvězd pro hlasování.
Průměrné hodnocení. 0 / 5. Počet hlasování: 0
Zatím nehodnoceno! Buďte první
Je mi líto, že pro Vás nebyl článek užitečný.
Jak mohu vylepšit článek?
Řekněte mi, jak jej mohu zlepšit.

Subscribe to the Newsletter
Stay informed! Join our newsletter subscription and be the first to receive the latest information directly to your email inbox. Follow updates, exclusive events, and inspiring content, all delivered straight to your email.
Are you interested in the WordPress content management system? Then you’ll definitely be interested in its security as well. Below, you’ll find a complete WordPress security guide available for free.

