Table of Contents:
- User roles in WordPress
- User role Subscriber
- User role Contributor
- User role Author
- User role Editor
- Main user roles in WordPress – Administrator
- Main user roles in WordPress – Super Administrator
- Where I can manage or create new user, with specific role in WordPress?
- More content about WordPress
Last updated December 6th, 2023 06:07
WordPress offers six pre-defined user roles that define the access level and permissions for different users who manage or contribute to a WordPress website. Here are the six default user roles in WordPress, listed in order of increasing level of access:
User roles in WordPress
Subscriber: This is the most basic user role in WordPress. Subscribers can only read content on the site and can’t create or edit content. They can, however, manage their own profile and leave comments.
Contributor: Contributors can write and manage their own posts, but they cannot publish them. Instead, they must submit their posts for review by an editor or administrator. Contributors can also edit their own profile information.
Author: Authors can create, publish, and manage their own posts, as well as edit their own profile information. They can also upload media files to the site.
Editor: Editors can create, publish, and manage their own posts, as well as edit and manage posts created by other users. They can also moderate comments, manage categories and tags, and upload media files to the site.
Administrator: Administrators have full control over the website. They can create and manage posts and pages, install and configure plugins and themes, manage users, and access all settings.
Super Administrator: This user role is available only in WordPress Multisite installations, where it allows a user to manage the entire network of sites.
It’s important to note that the specific permissions and capabilities associated with each user role can vary depending on the site’s settings and any plugins or customizations that have been added. In addition, WordPress allows site administrators to create custom user roles and assign specific capabilities to those roles. This can be helpful in creating more fine-grained access controls that are tailored to the needs of a particular website or organization.
User role Subscriber
In WordPress, the Subscriber role is the most basic user role available. Subscribers have limited permissions and can only interact with the website in a limited way. Here’s an overview of the permissions associated with the Subscriber role in WordPress:
Reading: Subscribers can read all public content on the website, including posts and pages. They can also access any custom post types that have been made public.
Commenting: Subscribers can leave comments on published content, but these comments must be approved by an editor or administrator before they appear on the site.
Profile management: Subscribers can manage their own profile information, such as their name, email address, and password.
Subscription management: If the site has a subscription feature, Subscribers can manage their own subscription settings and preferences.
No editing or publishing: Subscribers cannot create, edit, or publish any content on the website.
Overall, the Subscriber role is primarily intended for users who want to stay informed about a website’s content and participate in the site’s community through commenting. However, because Subscribers have no ability to create or modify content, their role is generally not relevant for users who need to contribute to the development or maintenance of a WordPress site.
User role Contributor
Contributor role is a user role that allows users to create and manage their own posts, but not publish them. Contributors can submit their posts to an editor or administrator for review and publishing. Here’s an overview of the permissions associated with the Contributor role in WordPress:
Writing: Contributors can create and manage their own posts, but cannot publish them. They can edit, save, and submit their posts for review, but cannot make them public without an editor or administrator’s approval.
Commenting: Contributors can leave comments on published content, but these comments must be approved by an editor or administrator before they appear on the site.
Profile management: Contributors can manage their own profile information, such as their name, email address, and password.
No editing or publishing of other content: Contributors cannot edit, publish, or delete any content created by other users, including posts, pages, or comments.
Media upload: Contributors can upload media files, such as images, videos, and audio files, to the site, but cannot manage or edit media files uploaded by other users.
The Contributor role is a good fit for users who want to contribute content to a WordPress site, but don’t need full publishing permissions. It can be useful for sites that require content moderation or review before it goes live, as well as for community-oriented sites that rely on user-generated content.
User role Author
Author role is a user role that allows users to create, manage, and publish their own posts. Here’s an overview of the permissions associated with the Author role in WordPress:
Writing: Authors can create and manage their own posts, and publish them without requiring further review or approval from an editor or administrator.
Commenting: Authors can leave comments on published content, but these comments must be approved by an editor or administrator before they appear on the site.
Profile management: Authors can manage their own profile information, such as their name, email address, and password.
Media upload: Authors can upload media files, such as images, videos, and audio files, to the site, and can manage and edit their own media files.
No editing or publishing of other content: Authors cannot edit, publish, or delete any content created by other users, including posts, pages, or comments.
The Author role is a good fit for users who create content for a WordPress site and have a high degree of editorial control over their content. It is ideal for bloggers, journalists, and other content creators who need to publish their own work on a regular basis. The Author role can also be useful for sites that require content moderation or review before it goes live, but where individual authors have a significant level of autonomy over their own content.
User role Editor
Editor role is a user role that has significant control over content on the site. Editors have the ability to create, edit, and publish posts and pages, as well as manage other users and content. Here’s an overview of the permissions associated with the Editor role in WordPress:
Writing: Editors can create, edit, and manage their own posts and pages, as well as those of other users. They can also publish and manage other users’ posts and pages.
Commenting: Editors can leave comments on published content, and can approve or delete comments left by other users.
Profile management: Editors can manage their own profile information, as well as the profile information of other users.
Media management: Editors can upload media files, such as images, videos, and audio files, to the site, and can manage and edit all media files uploaded by any user.
User management: Editors can create, edit, and delete user accounts, as well as manage user roles and permissions.
Theme and plugin management: Editors can install, activate, and deactivate themes and plugins, as well as configure their settings.
No access to site settings: Editors cannot modify site settings, such as those related to site address, language, and time zone.
The Editor role is a good fit for users who have significant editorial control over a WordPress site. It is ideal for sites with multiple authors or for content-heavy sites that require a high degree of content management. The Editor role can also be useful for sites where a single user needs to manage all aspects of the site’s content, including user accounts, media files, and site updates.
Main user roles in WordPress – Administrator
Administrator role is the highest level of user role and has complete control over the site. Administrators have the ability to manage all aspects of a WordPress site, including creating and managing content, configuring site settings, and managing user accounts. Here’s an overview of the permissions associated with the Administrator role in WordPress:
Writing: Administrators can create, edit, and manage all posts and pages on the site, as well as those of other users. They can also publish and manage other users’ posts and pages.
Commenting: Administrators can leave comments on published content, and can approve or delete comments left by other users.
Profile management: Administrators can manage their own profile information, as well as the profile information of other users.
Media management: Administrators can upload media files, such as images, videos, and audio files, to the site, and can manage and edit all media files uploaded by any user.
User management: Administrators can create, edit, and delete user accounts, as well as manage user roles and permissions. They can also reset passwords and edit any user’s profile information.
Theme and plugin management: Administrators can install, activate, and deactivate themes and plugins, as well as configure their settings.
Site settings: Administrators can modify all site settings, including those related to site address, language, and time zone. They can also configure site settings related to permalinks, privacy, and site optimization.
Database management: Administrators have access to the site’s database and can manage its tables and content.
The Administrator role is a good fit for users who need complete control over a WordPress site, including content creation, management, and site configuration. It is ideal for site owners, webmasters, or developers who need to manage all aspects of a WordPress site. However, it is important to be cautious when granting administrator access to other users, as this role has the ability to make significant changes to the site and its content.
Main user roles in WordPress – Super Administrator
“Super Administrator” typically refers to a role that exists in the context of WordPress Multisite, which is a feature that allows multiple WordPress sites to be managed from a single installation. In a Multisite environment, the Super Administrator is the highest level of user and has complete control over all sites within the network.
The Super Administrator has all of the same permissions as a regular Administrator in WordPress, with the addition of a few extra capabilities that are specific to Multisite. These capabilities include:
Site creation: Super Administrators can create new sites within the network and manage their settings.
User management: Super Administrators can create, edit, and delete user accounts on any site within the network, as well as manage user roles and permissions.
Site management: Super Administrators can manage all aspects of any site within the network, including content creation, management, and site configuration.
Network-wide settings: Super Administrators can modify settings that affect the entire network, such as site address, language, and time zone. They can also configure network-wide settings related to permalinks, privacy, and site optimization.
Plugin and theme management: Super Administrators can install, activate, and deactivate plugins and themes network-wide, as well as configure their settings.
Database management: Super Administrators have access to the database that powers the entire network and can manage its tables and content.
The Super Administrator role is a good fit for users who need to manage multiple WordPress sites from a single installation. It is ideal for site owners, webmasters, or developers who need to manage multiple sites within a network. However, as with the Administrator role, it is important to be cautious when granting Super Administrator access to other users, as this role has the ability to make significant changes to the entire network and its content.
Where I can manage or create new user, with specific role in WordPress?
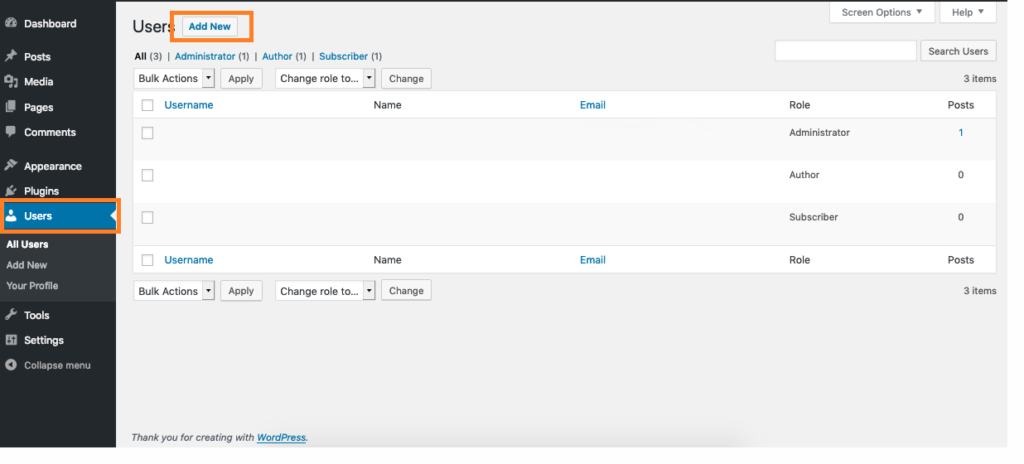
In WordPress, you can manage users and create new users with specific roles from the Users menu in the WordPress dashboard. Here’s how to do it:
- Log in to your WordPress dashboard.
- Click on the Users menu in the left-hand sidebar.
- From here, you can view a list of all the users on your site, along with their roles and some basic information about their accounts.
- To add a new user, click on the Add New button at the top of the page.
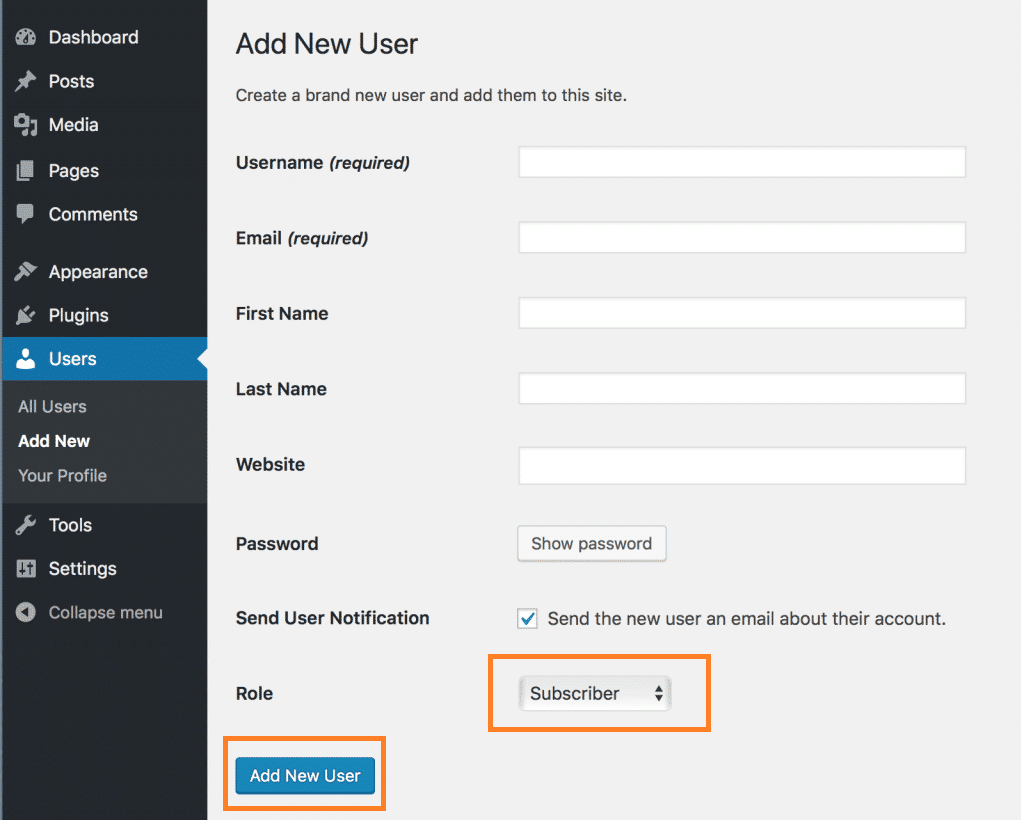
- Fill in the user’s details, including their username, email address, and password. You can also assign them a role by selecting the appropriate option from the Role dropdown menu.
- Once you’ve filled in all the necessary details, click on the Add New User button to create the new user.
If you need to change the role of an existing user, you can do so by following these steps:
- From the Users menu, find the user you want to edit and click on their username to open their profile page.
- From here, scroll down to the Role dropdown menu and select the new role you want to assign to the user.
- Click on the Update User button to save your changes.
It’s important to be careful when assigning user roles, especially if you’re giving someone access to sensitive areas of your site. Make sure you only give users the level of access they need to do their job, and avoid assigning them a role with more permissions than they require.
The website is created with care for the included information. I strive to provide high-quality and useful content that helps or inspires others. If you are satisfied with my work and would like to support me, you can do so through simple options.
Byl pro Vás tento článek užitečný?
Klikni na počet hvězd pro hlasování.
Průměrné hodnocení. 0 / 5. Počet hlasování: 0
Zatím nehodnoceno! Buďte první
Je mi líto, že pro Vás nebyl článek užitečný.
Jak mohu vylepšit článek?
Řekněte mi, jak jej mohu zlepšit.

Subscribe to the Newsletter
Stay informed! Join our newsletter subscription and be the first to receive the latest information directly to your email inbox. Follow updates, exclusive events, and inspiring content, all delivered straight to your email.
Are you interested in the WordPress content management system? Then you’ll definitely be interested in its security as well. Below, you’ll find a complete WordPress security guide available for free.

